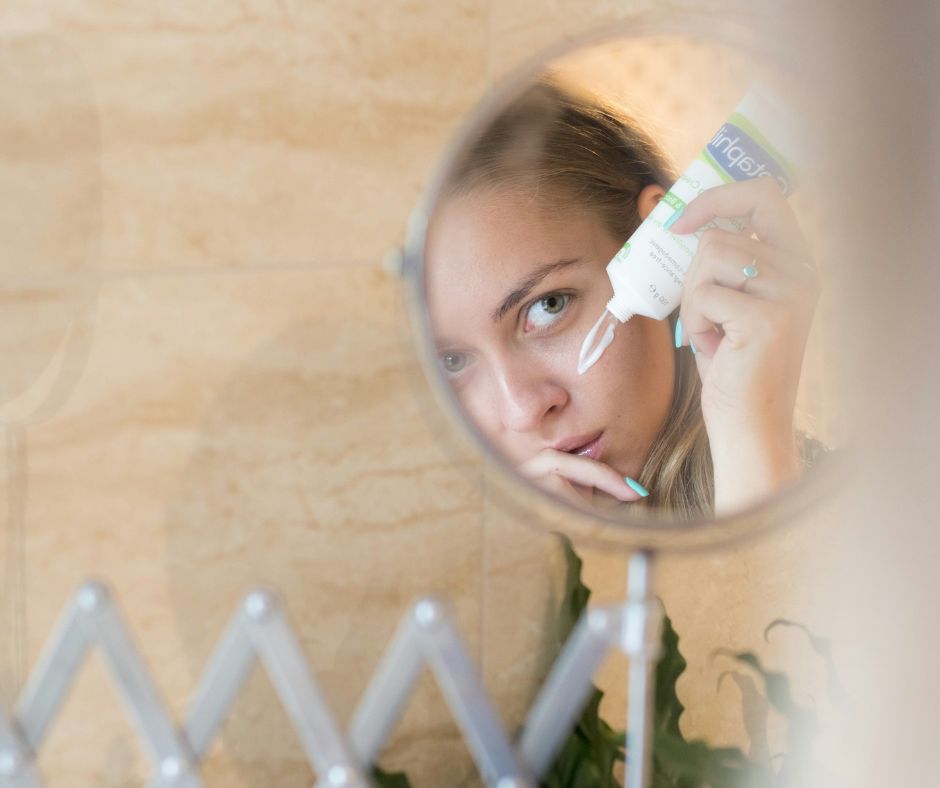
The European Commission has recently adopted a new regulation that will impact the use of vitamin A in cosmetic products, including skincare items containing retinol and tretinoin. This regulation, set to come into force in 2025, aims to ensure consumer safety while balancing the benefits of vitamin A with its potential risks.
Background to the regulation of retinol
Vitamin A, also known as retinol, is a vital nutrient necessary for the normal function of vision, skin, and mucous membranes. It has long been a popular ingredient in skincare products due to its rejuvenating properties, often marketed for its ability to reduce wrinkles and improve skin texture. However, scientific studies have shown that excessive exposure to vitamin A can pose risks to health.
The Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS) has conducted extensive research and concluded that while vitamin A is safe in cosmetic products at certain concentrations, it can contribute to overall exposure levels that may raise concerns for some consumers.
New concentration limits and labeling requirements for retinol
Under the new EU regulation, the following rules will apply:
- Concentration limits: The maximum concentration of retinol used in facial skin care will be 0.3% and 0.05% in body lotions.
- Mandatory labeling: All cosmetic products containing retinol, retinyl acetate, or retinyl palmitate must be labeled with the statement: “Contains Vitamin A. Consider your daily intake before use.”
- Implementation timeline: From November 1, 2025, products that do not comply with the new regulations will no longer be allowed on the EU market.
Impact on the skincare industry
This regulation will have significant effects on the skincare industry, especially for products marketed for their anti-aging benefits:
- Product reformulation: Many companies will need to reformulate their products to meet the new concentration limits for vitamin A. This could mean reducing the amount of retinol in certain products or finding alternative ways to achieve similar results without exceeding the allowed concentration.
- Increased costs: Reformulating products and updating labeling to comply with the new regulations will lead to increased production costs for manufacturers. These changes may also result in delays in bringing products to market.
- Consumer awareness: The mandatory labeling requirement is expected to raise consumer awareness about their total vitamin A intake from skincare products. It may prompt users to be more mindful of the cumulative effects of using multiple products containing vitamin A.
- Alternative ingredients: In response to these new limits, some companies may explore alternative anti-aging ingredients to complement or replace retinol in their formulations. This could lead to an increase in the popularity of ingredients like peptides, antioxidants, and other retinol alternatives.
While the new regulation may present challenges for the skincare industry, it is designed to ensure the safe use of vitamin A in cosmetic products. Consumers will continue to benefit from the skin-rejuvenating effects of vitamin A, but with added safety and awareness regarding their total exposure.
Read more about longevity
Leading Longevity Biotech Companies and Technologies 2025
Age-related diseases account for over 50 percent of the global disease burden. A report from…
How Human Lifespan Doubled
The human lifespan has changed dramatically over the past centuries. From an average of 30–40…
7 Animals That Defy Aging
Scientists have long been fascinated by animals that seem to defy aging. While most species…
How to Measure Biological Age with Epigenetic Clocks: The Power and Pitfalls
Your biological age says more about your health than your chronological age. While chronological age…
Outpace the Aging Process: Longevity Escape Velocity
Imagine living long enough for advancements in science and technology to surpass the aging process…